Stock Delisting vs. Stock Suspension: Key Differences Explained
Jan 18, 2024 By Triston Martin
Understanding the distinctions between stock delisting and stock suspension is crucial. Delisting a company's shares permanently removes them from a stock exchange. The company's exit from the market or inability to meet exchange requirements may cause this. A prominent American firm was delisted in 2021 for financial reporting violations.
Stock suspensions are temporary halts to a company's share trading. This happens when major corporate events or regulatory investigations affect the stock price. In 2020, the stock trading of a large UK company was temporarily halted after a major acquisition.
These measures will have major effects. The data shows that 10% of stocks suspended on major stock exchanges never reopen, which can deplete investors' strategies. Stock market investors must monitor these differences to make informed decisions and protect investments.
Stock Delisting
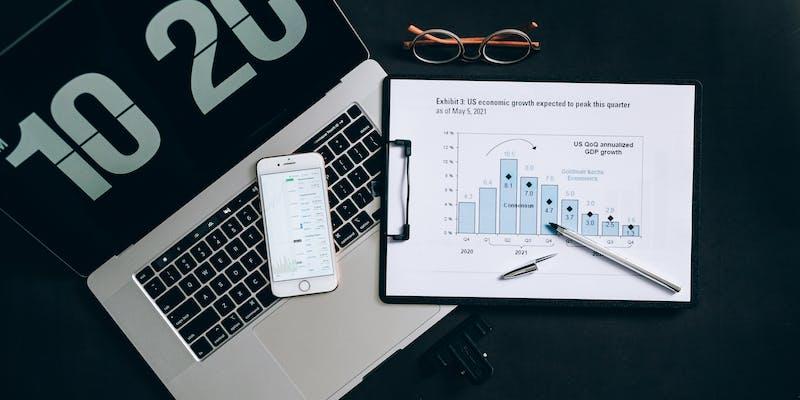
Without stock exchange trading, a company's shares are delisted. This change removed the company from public markets. Delisting stock has many causes. A company may be struggling financially or undergoing a merger. The stock exchange may delist a company that no longer meets its criteria.
Delisting has major effects. This makes it harder for shareholders to trade shares, making their investment less liquid. This usually means the company's status or finances have declined. Delisting stock can affect the market by changing investor perceptions of comparable stocks or industries. Delisting has increased in some industries in recent years. Tech delistings have increased over the past five years due to the industry's rapid change and market volatility. This shows the importance of understanding the stability and conformity of unpredictable businesses.
Stock delisting removes a company's shares from a stock exchange. When a company fails financial or regulatory requirements, the exchange often initiates this process. Consider China Mobile. The NYSE delisted the Chinese telecoms giant in 2019 due to U.S. executive orders highlighting national security risks. It affected the company's ability to attract US investors and the geopolitical climate.
Financial problems may lead to delisting. J.C. Penney was near delisting from the NYSE in 2020 after filing for bankruptcy. The fact that their stock value fell below the minimum required price showed their financial instability. Delisting damages a company's fundraising and investor trust. Companies sometimes voluntarily delist from one exchange for strategic reasons like cost savings, which does not necessarily indicate financial trouble.
Reasons For Stock Exchange Removal
Company delisting is the removal from a stock exchange. Several reasons could cause this. The process is crucial to the company and its investors. This article discusses the most common reasons for company stock delisting.
Unsatisfied List requirements
Failure to meet exchange listing standards is the main reason for stock delisting. Stock exchanges set minimum market capitalization, share price, and financial report frequency. Companies that can't adapt risk extinction. A company may lose NYSE eligibility if its shares consistently trade below $1.
Financial Troubles Leading to Bankruptcy
A company that is undergoing bankruptcy is frequently delisted. The bankruptcy signifies severe financial distress, which typically signifies that the company is no longer eligible to meet the listing requirements.
Violating Regulations
A company that violates significant laws or regulations risks expulsion from the exchange. Serious transgressions such as insider trading or falsified financial reporting frequently constitute grounds for this form of delisting.
Company Mergers and Acquisitions
Frequently, delisting results from a merger or acquisition of a company. This occurs because the initially listed company no longer operates autonomously and, as such, may meet the requirements of the listing.
Other Factors
There are additional, less frequent motives for stock delisting. A company may elect to go private at times, or its stock may be delisted if it is determined that it is no longer suitable for exchange trading.
Trading Suspension
Trading suspension is slightly different. It occurs when the stock market temporarily halts company share trading. No one can buy or sell company shares during this suspension. Major events that could affect the firm's share price usually prompt a pause. Stock exchanges or regulatory agencies do this to protect investors and give them time to understand and respond to news. Trading may be suspended if a company reports unexpectedly low earnings or is scandalized. Without irrational selling or buying, the market can digest this information.
Share trading stops when a company's shares are suspended. News announcements or regulatory concerns can cause a suspension. Social media purchases caused GameStop's stock to fluctuate, resulting in multiple NYSE suspensions in 2021. This incident showed how social media and modern trading platforms affect stock prices.
German payment processor Wirecard had its London Stock Exchange shares suspended in 2020. The €1.9 billion accounting scandal was known. Suspensions are usually imposed to protect investors from stock movements caused by incomplete or uncertain information.
Reason For Trading Suspensions
Upcoming Announcements
Before a company announces major news that could affect its stock value, trading in its shares is usually halted. This step ensures that all investors use the same information when making decisions. This news can cover mergers and acquisitions, financial results, and other major economic events.
Trade Cessation Due
Questions about a company's regulatory compliance can also halt trading. Fraud, insider trading, and market manipulation should not be ignored. Market integrity and investor protection require these suspensions.
The SEC implemented a notable measure 2015 when it suspended trading in 128 inactive shell companies. This path of action changed into carried out as a precaution against potential pump-and-dump schemes, which contain the artificial inflation of stock costs followed by their profitability, which often leads to vast losses for uninformed traders.
Financial Difficulties
Financially struggling companies may also stop trading. This was done to protect investors from losses and prevent panic selling. It gives the struggling business time to restructure, talk to creditors, or file for bankruptcy.
For example, the Hong Kong Stock Exchange suspended China Ding Yi Feng Holdings Limited in 2019. When the firm didn't release its annual report and financial accounts, concerns about its financial stability and transparency increased.
Technical Trading Problems
Technical issues with the stock exchange or trading platforms can suspend trading. System failures and connectivity issues can halt operations until resolved. Due to system issues, the New York Stock Exchange suspended Amazon and Alphabet trading in 2020. This was necessary to prevent technical issues-related fraud.

May 08, 2024 Triston Martin

Sep 08, 2024 Sid Leonard

Jan 18, 2024 Triston Martin

Mar 20, 2024 Susan Kelly

Oct 17, 2023 Susan Kelly

May 18, 2024 Susan Kelly